湖泊超微型浮游藻类研究取得重要进展
超微型浮游藻类(粒径 ≤ 3 μm),简称超微藻,广泛分布于海洋和淡水生态系统中,在水生生态系统尤其是微食物环中起着重要作用。它们具有更高的CO2固定效率,对水体初级生产力的贡献量可高达90%,并且其潜在的混合营养代谢功能对浮游细菌的种群具有重要调控作用。目前有关超微藻的研究主要集中在海洋,对湖泊超微藻的研究仍较少,现有认知非常有限。中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所史小丽研究小组在国家自然科学基金的长期资助下,对湖泊超微藻开展了持续研究,通过结合流式细胞技术和高通量测序技术对太湖、巢湖、鄱阳湖、抚仙湖等湖泊中超微藻丰度、初级生产力水平及其多样性和群落结构的时空分布特征进行了系统研究,取得了一系列重要研究成果。
(1)首先开发了流式分选和高通量测序相结合的方法,能更快速和深入的揭示超微真核藻的群落结构特征。由于异养微生物多样性高,目前常用的利用滤膜过滤收集超微藻并测序的方法,得到的结果通常以异养微生物序列为主,不利于光合自养超微藻多样性的研究。本方法首先采用流式细胞术,根据藻类的自发荧光将自养超微藻分选出来,然后针对分选样品进行高通量测序,该方法将自养超微藻序列在总序列的比例提高2倍,大大提高了对超微藻的认知水平。发现了新超微藻种群Prasinophyceae Clade IX,并在湖泊中发现了以前认为仅在海洋存在的Ostreococcus;
(2)超微藻对湖泊初级生产力有重要的贡献,其全年平均贡献率随着湖泊营养盐水平的上升而下降,在抚仙湖、鄱阳湖和巢湖分别达到65%,60%和23%;
(3)湖泊超微藻丰度高,多样性丰富,主要包括真核超微藻(Photosynthetic Picoeukaryotes),富含藻蓝素的超微蓝藻(Phycocyanin Picocyanobacteria)和富含藻红素的超微蓝藻(Phycoerythrin Picocyanobacteria),超微真核藻和富含藻蓝素的超微蓝藻在富营养湖泊优势度更高,具有互补的生态位,前者在冬春季和营养水平相对高的湖区占优势,后者在夏秋季和营养水平相对低的湖区占优势,而富含藻红素的超微蓝藻主要存在于贫营养湖泊;
(4)湖泊超微蓝藻主要为聚球藻(Synechococcus),而超微真核藻的多样性极高,分布于各大藻类门中,其中富营养湖泊中的优势种主要分布在绿藻门(Chlorophyta),硅藻门(Bacillariphyta)和隐藻门(Cryptophyta),贫营养湖泊中的优势种主要分布在金藻门(Chrysophyta)和定鞭藻门(Haptophyta)。在同一湖泊中,温度是影响超微藻群落结构演替的重要因子;
(5)高通量测序结果表明,即使是根据藻类自发荧光信号,利用流式细胞仪分选出超微藻真核藻细胞,测序后仍发现了大量异养微生物序列,主要包括Chytridiomycota、Perkinsozoa、Ciliophora以及Cercozoa等,表明了寄生和捕食等生物影响在超微真核藻群落变化中的重要作用。
相关研究成果在Environmental Microbiology,FEMS Microbiology Ecology,PLoS ONE,Journal of Plankton Research等本领域重要期刊上发表。
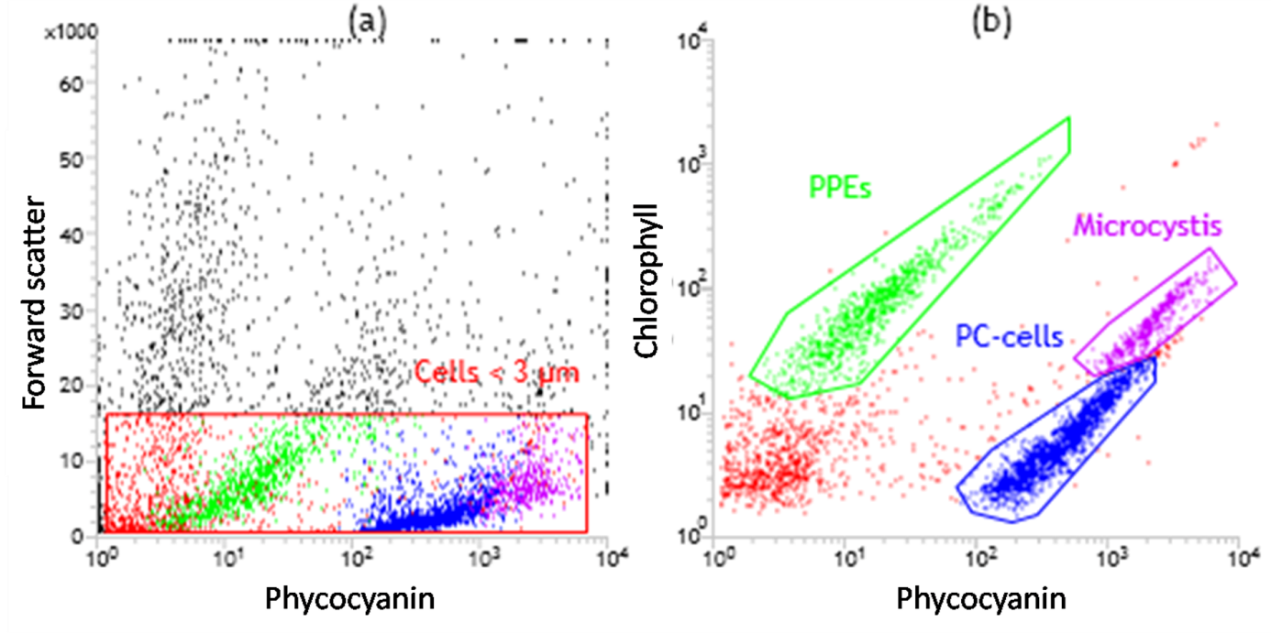
图1. 超微藻的流式细胞分选图
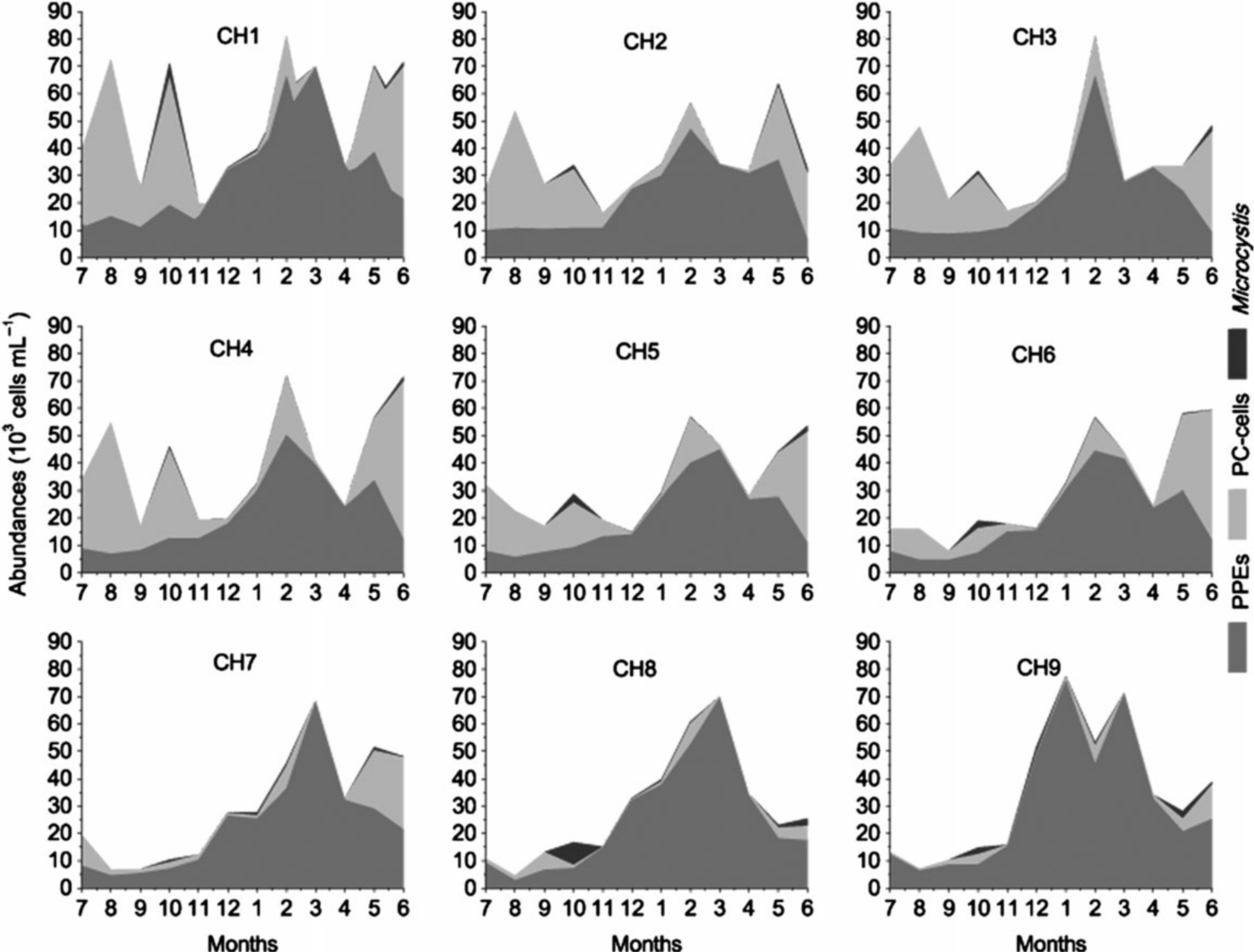
图2. 巢湖不同类型超微藻和单细胞微囊藻的时空分布特征

图3. 巢湖不同季节样品超微真核藻的群落结构
发表的相关文章:
1. Xiaoli Shi*, Shengnan Li, Fan Fan, Min Zhang, Zhen Yang and Yunfeng Yang, Mychonastes dominates the photosynthetic picoeukaryotes in Lake Poyang, a river-connected lake. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 2018. doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiy211. (2区)
2.Xiaoli Shi*, Shengnan Li, Changqing Liu, Min Zhang, Mixue Liu, Community structure of photosynthetic picoeukaryotes differs in lakes with different trophic statuses along the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 2018. doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiy011. (2区)
3. Shengnan Li, Gisele Bronner, Cecile Lepere, Fanxiang Kong and Xiaoli Shi*. Temporal and Spatial variations in the composition of freshwater photosynthetic picoeukaryotes revealed by MiSeq sequencing from flow cytometry sorted samples. Environmental Microbiology. 2017,19(6):2286-2300. (2区)
4. Shengnan Li?, Xiaoli Shi?*, CéCile Lepère, Mixue Liu, Xiujuan Wang and Fanxiang Kong.. Unexpected predominance of photosynthetic picoeukaryotes in shallow eutrophic lakes. Journal of Plankton Research. 2016.(2区)
5. Shengnan Li, Jian Zhou, Lijun Wei, Fanxiang Kong, Xiaoli Shi*. The effect of elevated CO2 on autotrophic picoplankton abundance and production in a eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China). Marine and Freshwater Research. 2016, 67:319-326.
6. Xiaoli Shi, Cécile Lepère, David J. Scanlan, Daniel Vaulot, Plastid 16S rRNA Gene Diversity among Eukaryotic Picophytoplankton Sorted by Flow Cytometry from the South Pacific Ocean. PLoS ONE. 2011, 6(4): e18979. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018979.(2区)
7.Dominique Marie, Xiaoli Shi, Fabret Rigaut-Jalabert, Daniel Vaulot. Use of flow cytometric sorting to better assess the diversity of small photosynthetic eukaryotes in the English Channel. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 2010, 72:165-178.
8. Xiaoli Shi, Dominique Marie, Ludwig Jardillier, David J. Scanlan. J. Daniel Vaulot. Groups without cultured representatives dominate eukaryotic picophytoplankton in the oligotrophic South East Pacific Ocean. PLoS ONE. 2009. 4(10):e7657.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007657.(2区)